
Evolutive iteration

Gallery Thesis
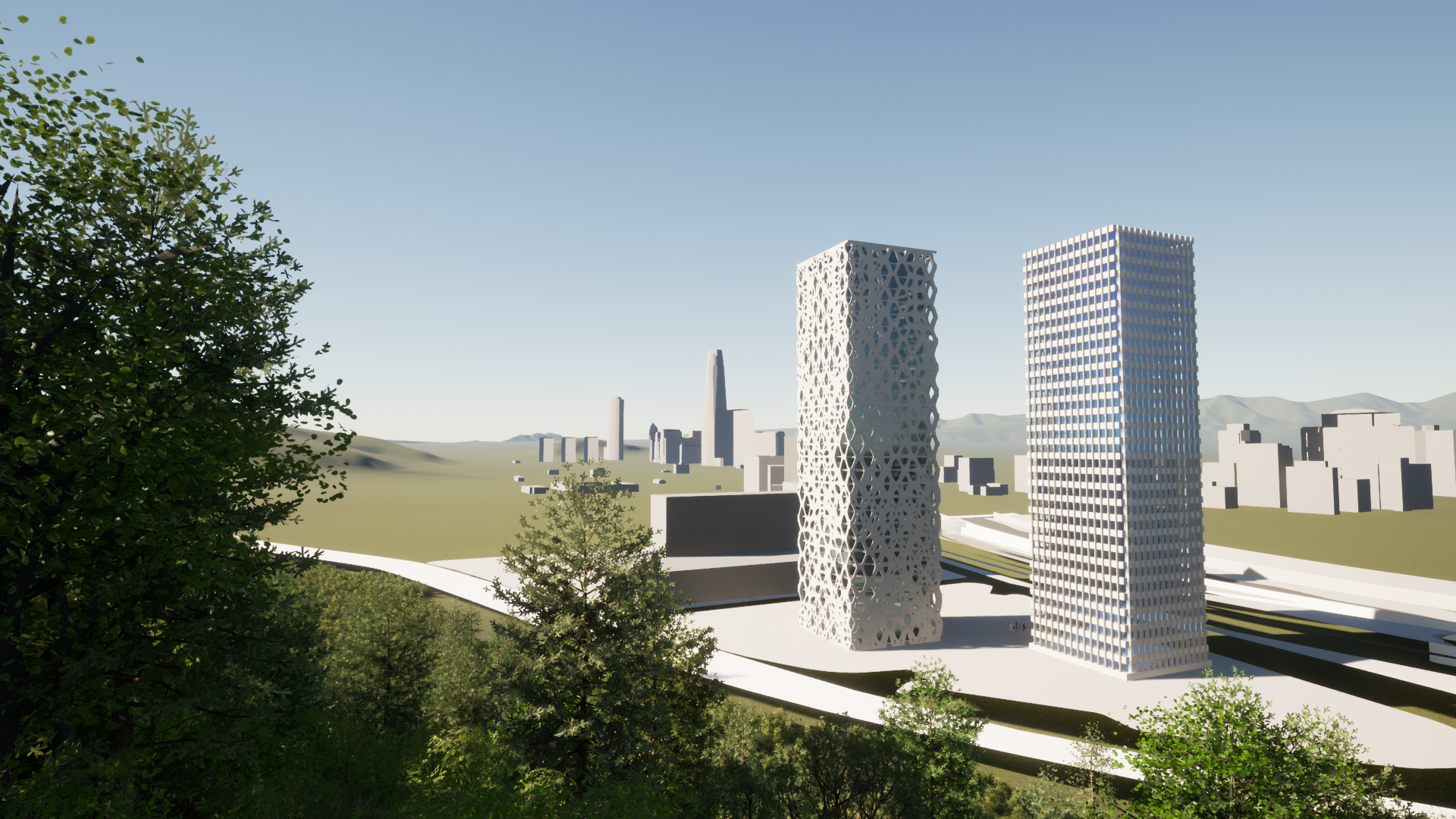
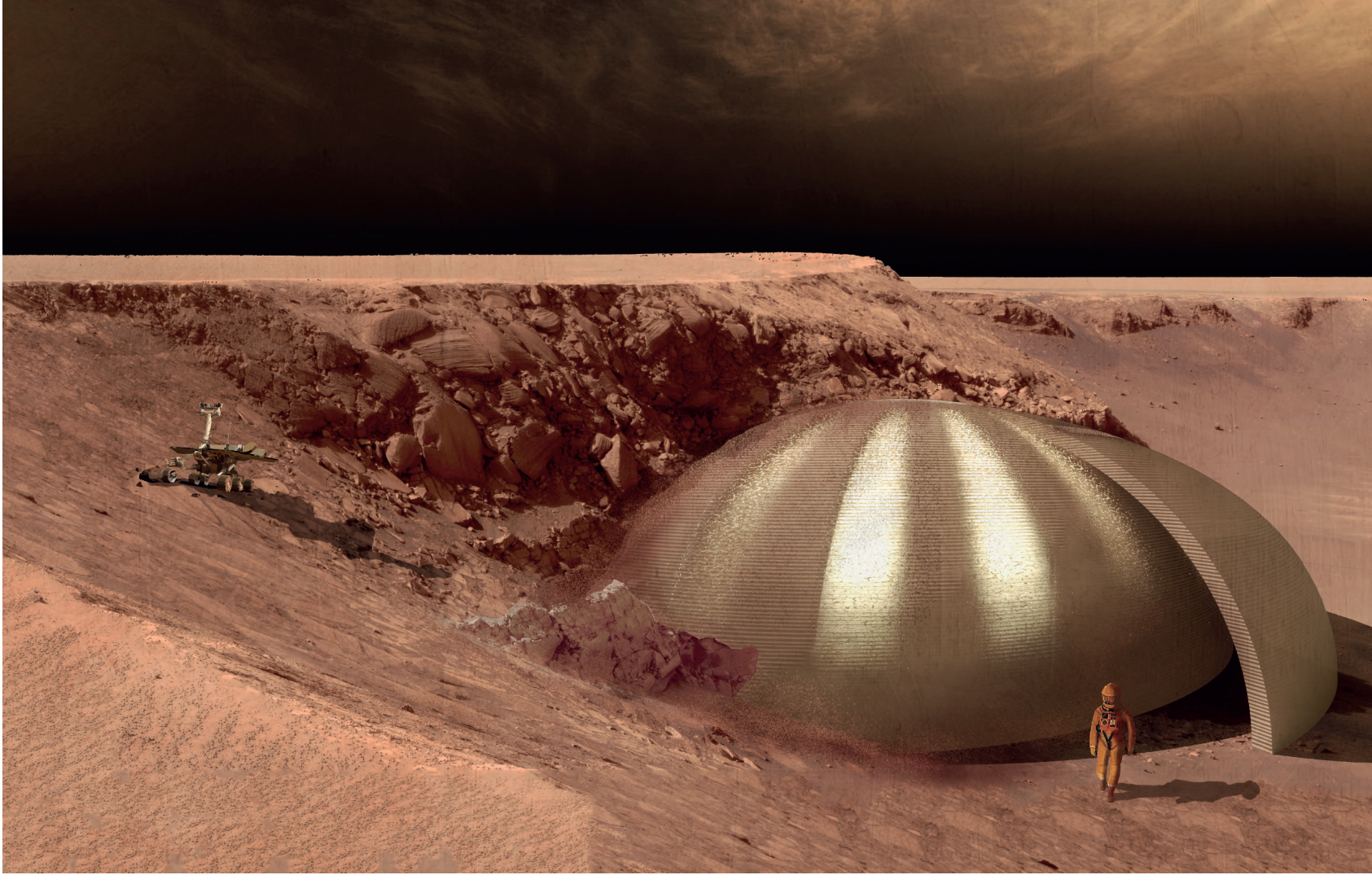
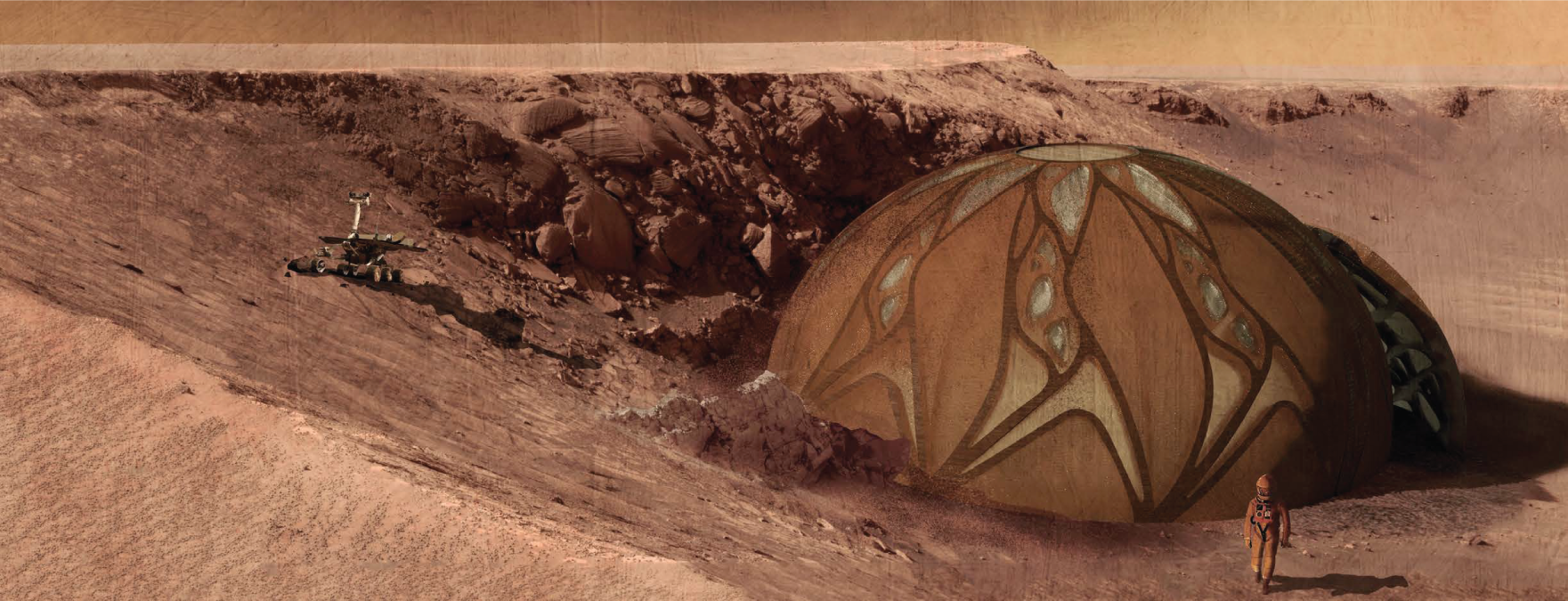
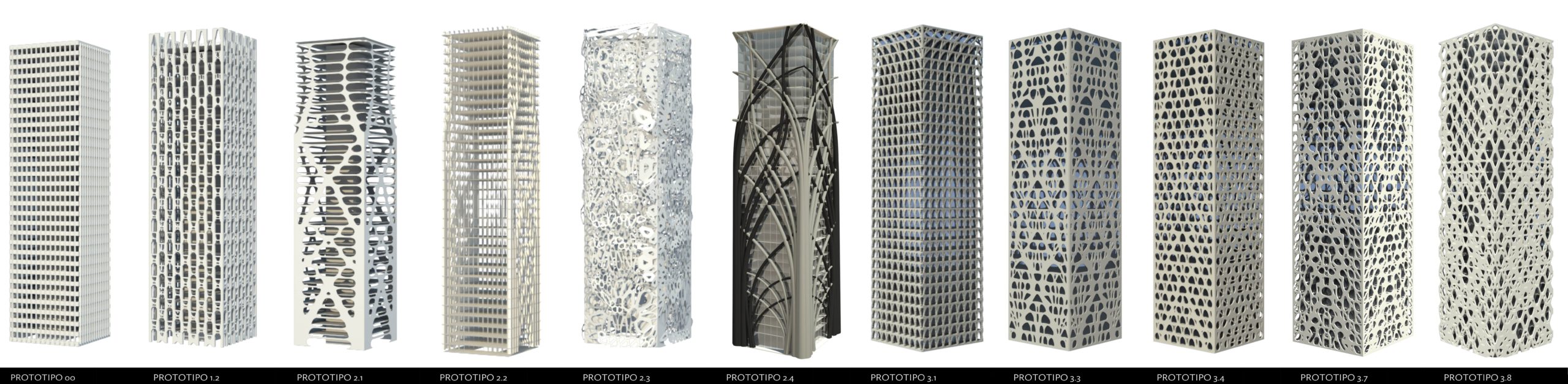
An evolutive approach progressed during the research. In other words, each time a new prototype was concluded, new questions about the scope of the combination of structural design with other variables arose, as well as the need to create a different and evolved prototype. An example of this experience was the evolution between the first and last facade models. In the previous, the overall and partial structural topology optimization were first implemented. In the latter, solar radiation, view analysis and digital fabrication were added. The thesis explored the opportunities allowed through a bottom-up approach, from working with algorithms and parametric tools. The research located practical work considerations while disciplinary discussions included “tall building” topology. The thesis situated the prototypes between the modernist, the postmodern and parametric styles of office tower paradigms. The results showcase an array of facade alternatives that evolved during the thesis process, leading to a parametric synthesis of facade performance variables.
Urban Occlusion
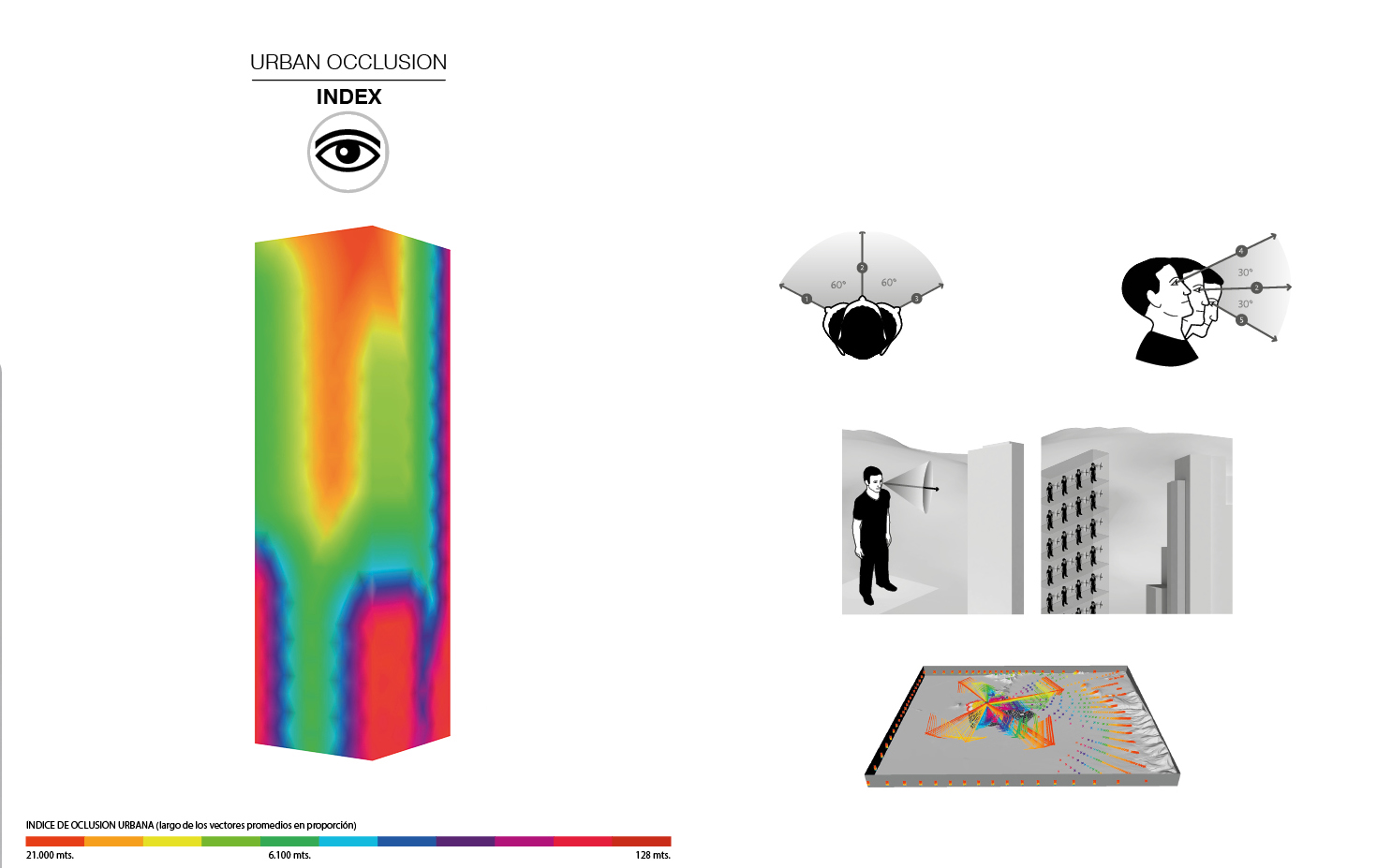
Urban Occlusion is an original script, I wrote entirely on Grasshopper ,based on Benedikt (1979). Isovists made in Grasshopper were used to measure the amount of vision over an array of cone angles from a given facade. This is an attempt to imitate human vision from the inside of a tower. This is possible by the addition of five vectors towards a 3D city model of Santiago de Chile, and their comparative index. Consequently, functional data is obtained to compare prototypes and design alternatives in order to open the facade toward the best views.
Solar Radiation
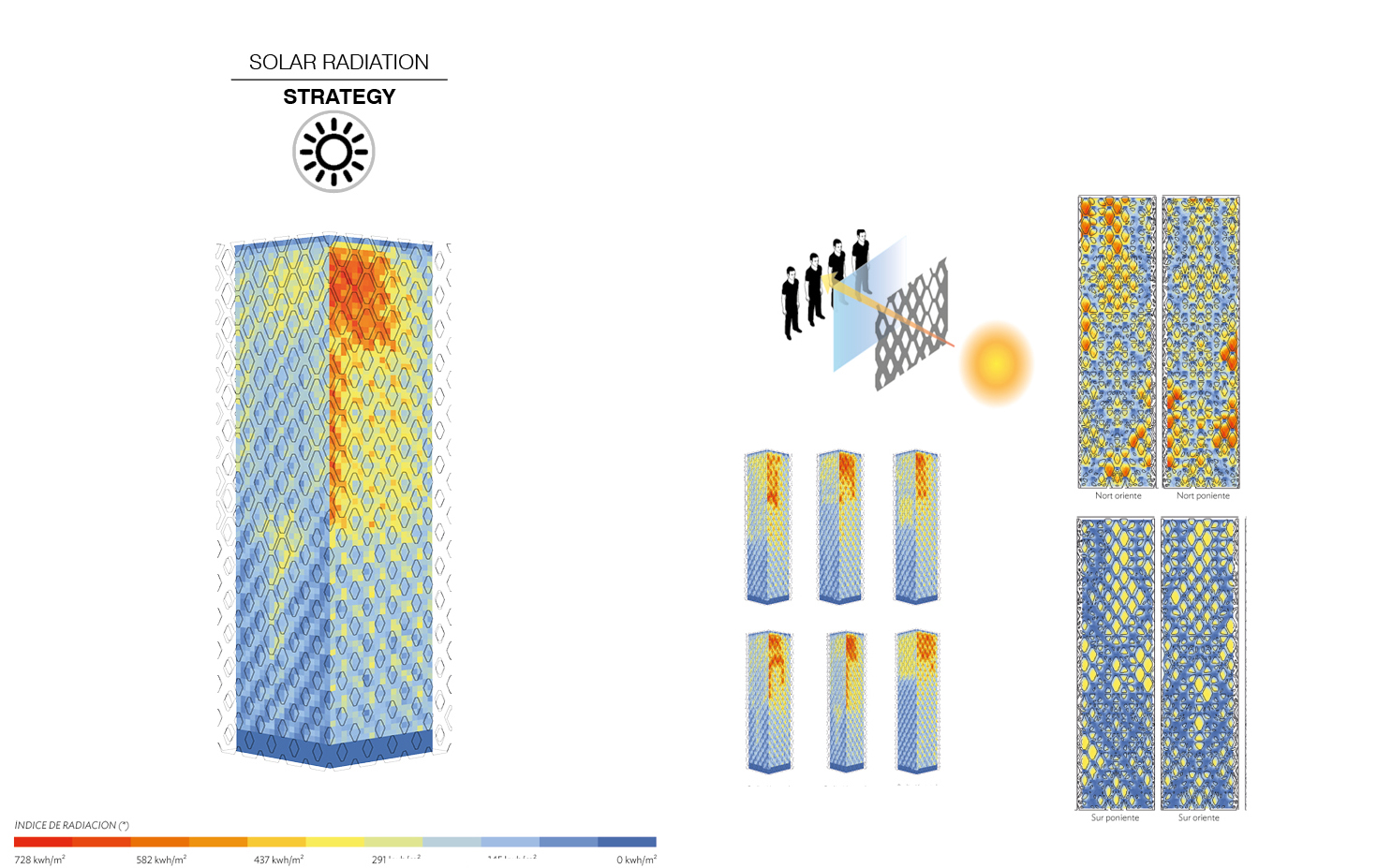
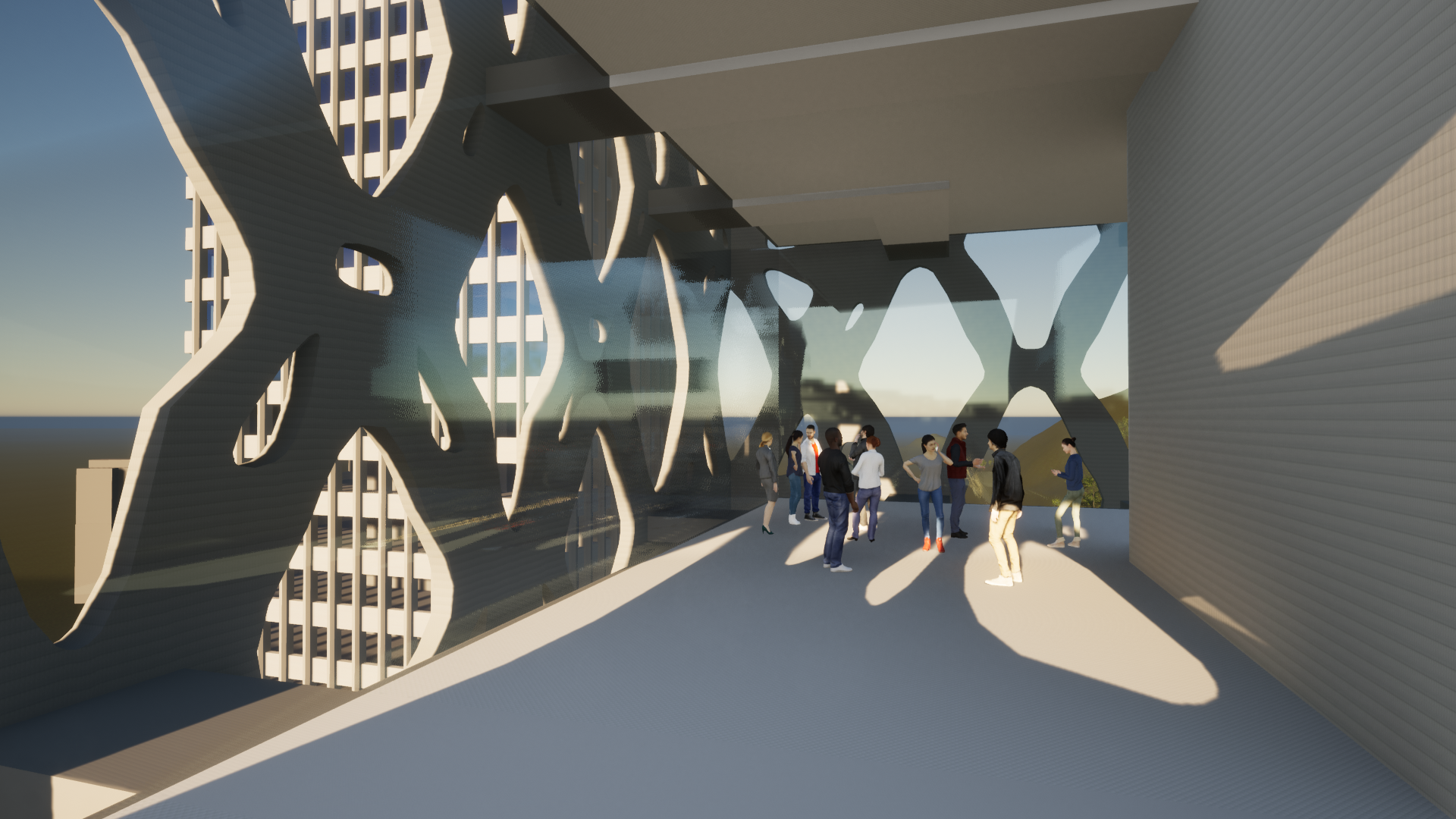
Solar radiation can be measured as the amount of energy a surface receives during a given time period. Due to the current global energy crisis, and the amount of energy used in cooling tall buildings, measuring heat gain is a pressing design variable. What’s more, early design strategies for solar radiation can significantly reduce this impact. Therefore, In the final prototype, direct solar radiation gain was reduced using the structural facade as a shading device over the glass facade with data-controlled openings towards city views
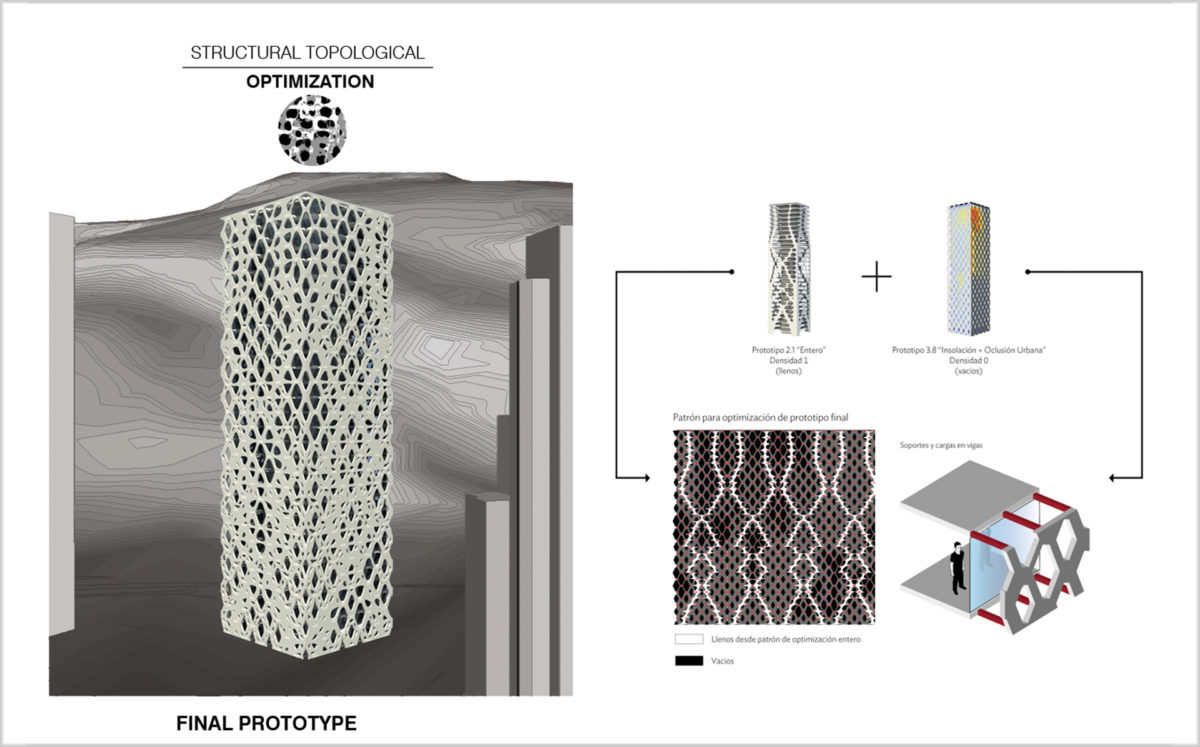
Structural Topological Optimization
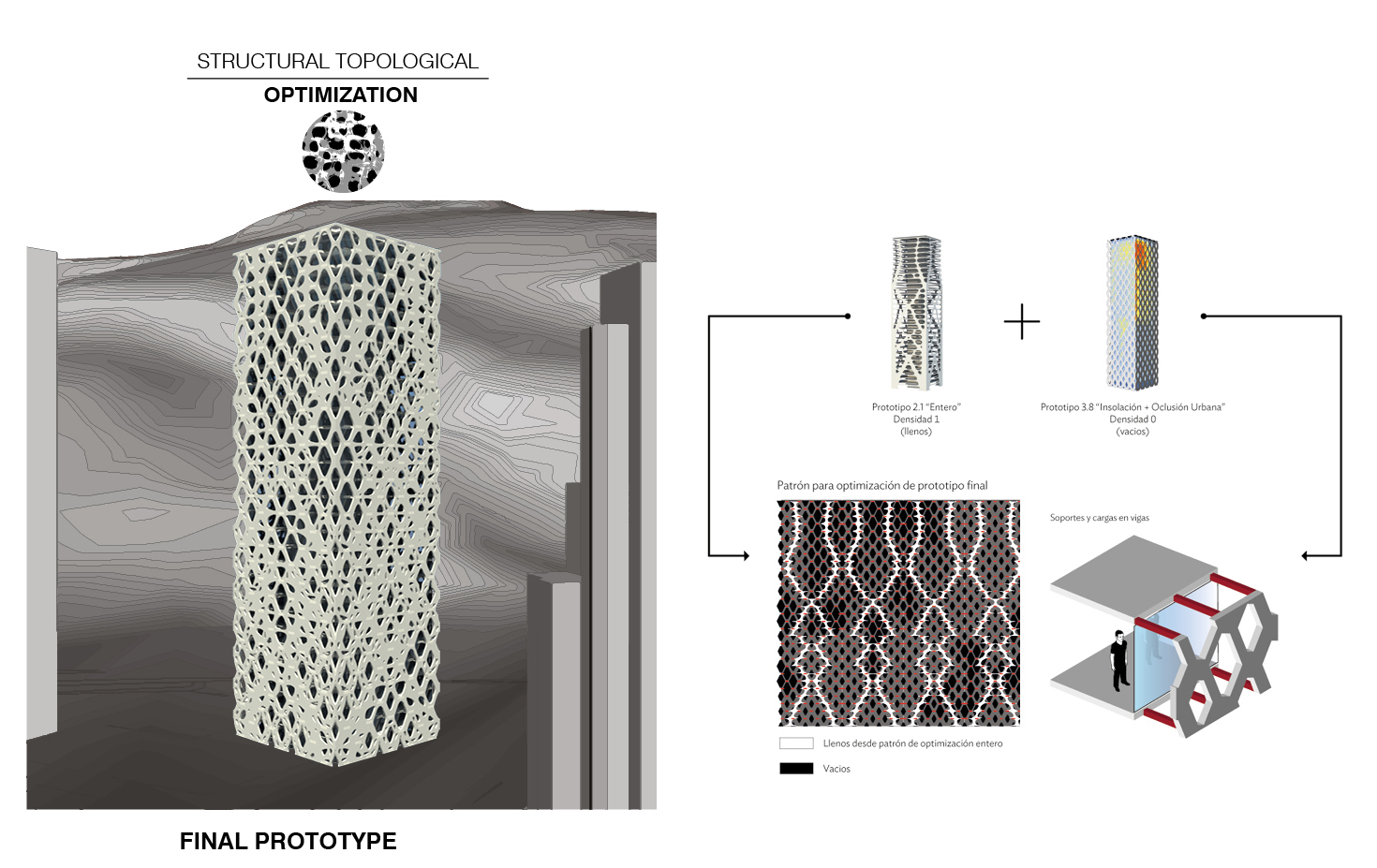
The previous process informed the final wall voids and restraint conditions render by structural topological optimization. This is performed by the combination of two algorithms, a complete facade script developed by Chilean academic research (Fondecyt 2011) and façade-level size by Millipede/Grasshopper plug-in (Sawako & Panagiotis). Finally, the outcoming geometry was discretized into an array of 25 shapes to be cut by CNC machines for concrete casting constructive parts.